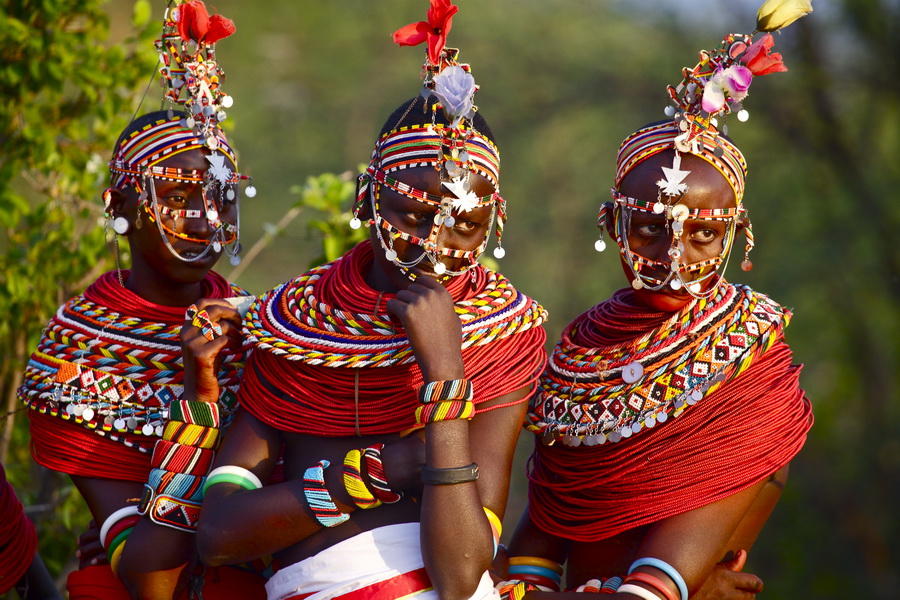
The Samburu people are some of the friendliest in Kenya. Originally a nomadic tribe, the Samburu today still embraces their nomadic culture while jointly running some of the best Kenya game lodges.
The Samburu tribe lives north of the equator in the geographically fascinating Samburu County of Northern Kenya.
The Samburu people are closely related to the Maasai tribe who also live in East Africa. Both these tribes speak a similar language, derived from Maa.
The Samburu, just like the Maasai are a semi-nomadic people. Only the Samburu are still very traditional and have not parted with old customs as compared to the Maasai. Cattle, as well as goats, sheep and camels, play a vital role in the Samburu way of life and culture.
The Samburu are highly dependent on their livestock for survival. Their diet comprises mostly of milk and occasionally blood from their cows.
The blood is accrued by slightly cutting the jugular of the cow, and draining the blood into a cup. The wound is then promptly sealed with hot ash.
Meat is only served on special occasions. The Samburu people’s diet is also supplemented with vegetables, roots and tubers that are made into a soup.
Traditional Samburu Culture
Samburu County is mostly dry barren land, and the Samburu tribe have to relocate to be certain their cattle have enough food.
Every few weeks the tribe will change location to find fresh grazing grounds. Huts are constructed using hide, mud, and grass mats strung over poles. A fence is built around the mud huts for protection from wild animals.
The Samburu tribe settlements are called manyattas.
The Samburu usually dwell in groups of five to ten families. Traditionally Samburu men look after their cattle and they are also responsible for the overall safety of the tribe.
Samburu women are responsible for gathering vegetables and roots, caring for their children and collecting water. Samburu girls usually help their mothers with domestic chores.
The Samburu are a gerontocracy, the elders rule the tribe. It is the elders that decide when ceremonies will occur, such as weddings and circumcisions.
Entry into womanhood and manhood is marked with a circumcision ceremony. Men and women are only able to get married once they have been circumcised, as prior to that they are still considered as children.
Once a boy has been circumcised he is now considered a Moran (a warrior). The men are placed into age sets, and as a group move from one social position to another. From child to Moran, to junior elder and finally to elder.
The traditional dress of the Samburu tribe is a striking red cloth wrapped like a skirt and a white sash. This is adorned with many colourful beaded earrings, bracelets, anklets and necklaces.
Each piece of jewellery worn represents the status of the wearer.
Dancing is a significant part of Samburu culture. Their dancing is similar to that of the Maasai people with men dancing in a circle and jumping high from a standing position. Traditionally, the Samburu have not used any instruments to accompany their dancing and singing.
The Samburu Today
Just like the Maasai tribe, the Samburu people are under pressure from their government to settle into more permanent villages.
They have resisted this proposal thus far since a permanent settlement would disrupt their entire way of life. And it will be difficult to grow and maintain crops on a permanent site.
Visiting the Samburu
The Samburu live in a very beautiful, sparsely populated part of Kenya with abundant wildlife. Much of the land is now protected and community development initiatives have extended to eco-friendly African lodges jointly run by the Samburu.
As a visitor, the best way to get to know the Samburu is to stay at a community-run lodge or enjoy a walking or camel safari with Samburu guides.